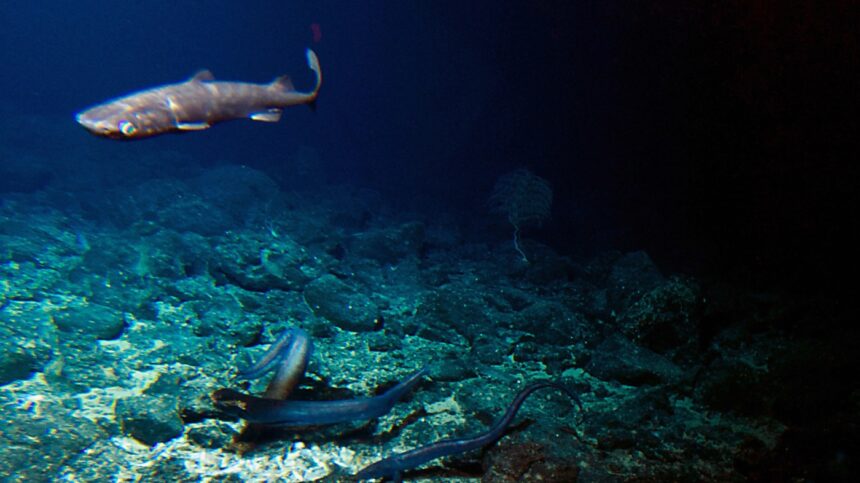
A deep sea shark and a number of other eels are interested in bait positioned on the summit of the Cook dinner seamount, as seen from the Pisces V submersible throughout a dive to the beforehand unexplored seamount off the coast of Hawaii’s Large Island on Sept. 6, 2016.
Caleb Jones/AP
disguise caption
toggle caption
Caleb Jones/AP
Researchers scouring the lightless panorama of the Pacific Ocean flooring suppose they’ve noticed “darkish oxygen” being created there, probably difficult generally held beliefs about how oxygen is produced on Earth.
Till now, it was thought that oxygen was created solely by photosynthesis, a course of that requires daylight. However the discovery casts doubt on that principle and raises new questions in regards to the origins of life itself.
“I believe we due to this fact have to revisit questions like: the place may cardio life have begun?” mentioned Andrew Sweetman, a professor with the Scottish Affiliation for Marine Science in Oban, Scotland, in a information launch.
The analysis group led by Sweetman printed its findings Monday in an article within the journal Nature Geoscience.
The scientists aren’t sure how oxygen is created at such darkish depths, however they consider it is being produced by electrically charged minerals referred to as polymetallic nodules, which vary in measurement from a small particle to in regards to the dimensions of a potato.
These nodules — “successfully batteries in a rock,” Sweetman mentioned — might use their electrical cost to separate seawater into hydrogen and oxygen in a course of referred to as seawater electrolysis.
“The traditional view is that oxygen was first produced round three billion years in the past by historic microbes referred to as cyanobacteria and there was a gradual improvement of advanced life thereafter,” mentioned the director of the Scottish Affiliation for Marine Science, Nicholas Owens, within the information launch. “The potential that there was another supply requires us to have a radical rethink.”
Researchers performed exams on the seafloor and in addition collected samples to check aboveground, and so they got here up with the identical consequence: that oxygen ranges elevated close to the polymetallic nodules.
Seawater may be cut up into hydrogen and oxygen with 1.5 volts of electrical energy, which is the quantity in a AA battery. Researchers discovered that a few of the nodules possessed as a lot as 0.95 volts of electrical energy, and a number of nodules collectively produced even larger voltages.
The invention may impression deep-sea mining
Polymetallic nodules include metals corresponding to manganese, nickel and cobalt, which can be utilized to make the lithium-ion batteries utilized in client electronics, home equipment and electrical automobiles.
Franz Geiger, a Northwestern College chemistry professor who labored on the examine, mentioned in a separate information launch that there could also be sufficient polymetallic nodules in an space of the Pacific Ocean referred to as the Clarion-Clipperton Zone to fulfill international power calls for for many years after.
However he additionally mentioned that mining must be performed in a means that didn’t get rid of oxygen for all times types in that a part of the ocean.
“We have to be actually cautious if it seems that deep-sea mining will develop into a possibility that is being pursued … that is completed on a stage and at a frequency that isn’t detrimental to life down there,” Geiger instructed NPR.
Corporations performed exploratory missions for deep-sea mining within the Seventies and ’80s, he mentioned, and up to date analysis means that these missions might have had repercussions on marine life within the space for many years.
“A couple of years in the past, a group of marine biologists went again to these areas that have been mined 40 years in the past and located primarily no life,” Geiger mentioned. “After which a couple of hundred meters over to the left and proper, the place the nodules have been intact, loads of life.”